
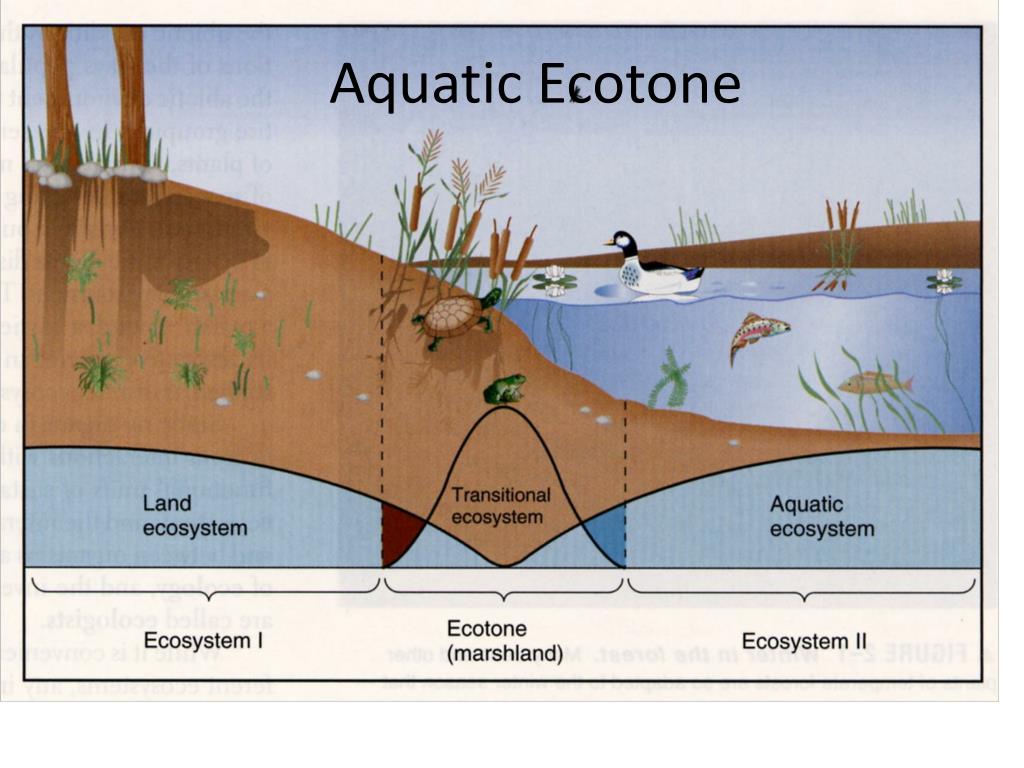
Ecocline occurs across the environmental gradient (gradual change in abiotic factors such as altitude, temperature (thermocline), salinity (halocline), depth, etc.).Ecocline is a zone of gradual but continuous change from one ecosystem to another when there is no sharp boundary between the two in terms of species composition.A well-developed ecotone contains some organisms which are entirely different from that of the adjoining communities.


#Ecotone edge effect Patch#
Note on the impact of the "pattern" of each patch of "color" on the "percolation capacities" of certain species in the landscape (compared to the surface considered). ) are similar, but the length of the ecotone between them varies greatly from case to case. In each case, yellow and green surfaces (schematically two different ecological habitats, eg the savannah and forest, or forest and water, or. This Image is a schematic representation of different types of ecotones on a square surface. * Richard Sennett, Building and Dwelling, Ethics for the City, Penguin Books Ltd, 2019
No transgression at the boundary: Keep Out! Which means the edge itself is dead.”

Whereas the boundary is a guarded territory, as established by prides of lions or packs of wolves. Not surprisingly, it is also at the borderline where the work of natural selection is the most intense. At borders, organisms become more inter-active, due to the meeting of different species or physical conditions for instance, where the shoreline of a lake meets solid land is an active zone of exchange where organisms find and feed off other organisms. The boundary is an edge where things end the border is an edge where difference groups interact. Gould, “who drew our attention to an important distinction in natural ecologies between two kinds of edges: boundaries and borders. Sennett illustrates his ideas by referring to paleontologist and evolutionary biologist Steven J. So we should want to build the border/membrane.” The result is that exchange between different racial, ethnic, or class communities diminishes. The most popular form of new residential development internationally, the gated community, takes to an extreme the idea of the boundary wall. The urban habitat is cut up into segregated parts by streams of traffic, by functional isolation between zones for work, commerce, family, and the public realm. According to sociologist Richard Sennett* “the boundary/wall dominates the modern city.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
